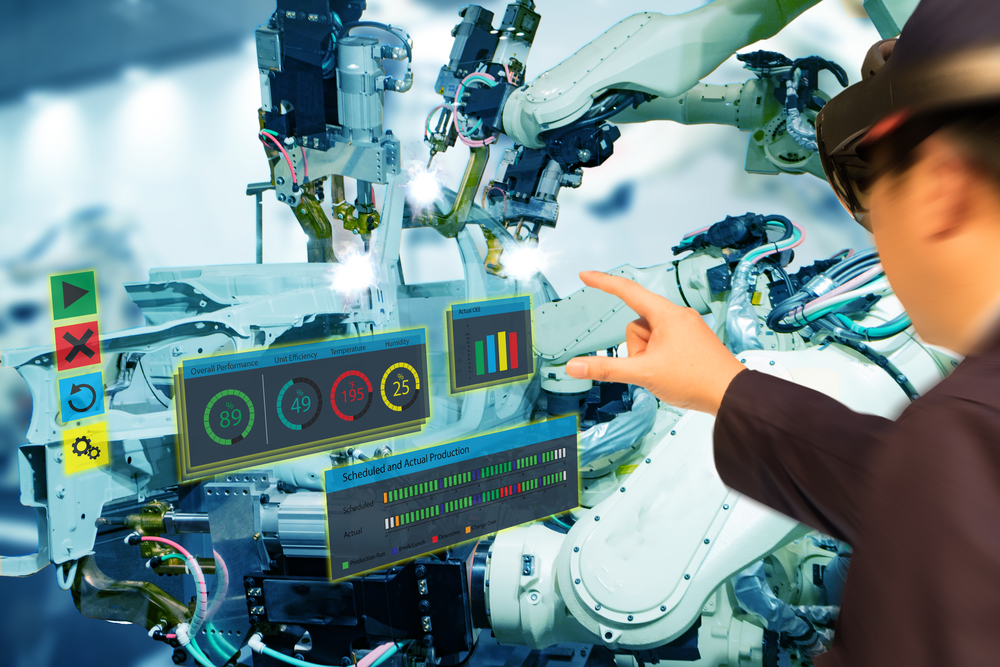
Augmented Reality, “an enhanced version of reality where live direct or indirect views of physical real-world environments are augmented with superimposed computer-generated images over a user’s view of the real world.”
The fourth industrial revolution is upon us and industries like manufacturing are taking advantage of AR technology to enhance employee experience, keep employees safer, and also close the knowledge gap.
Maintenance plays a vital role in industries like manufacturing. It has a direct influence on performance, productivity, and product quality; maintenance is a craft that is always being improved upon and now with the innovation of augmented reality, it can take maintenance to a whole other level.
Augmented Reality in Maintenance
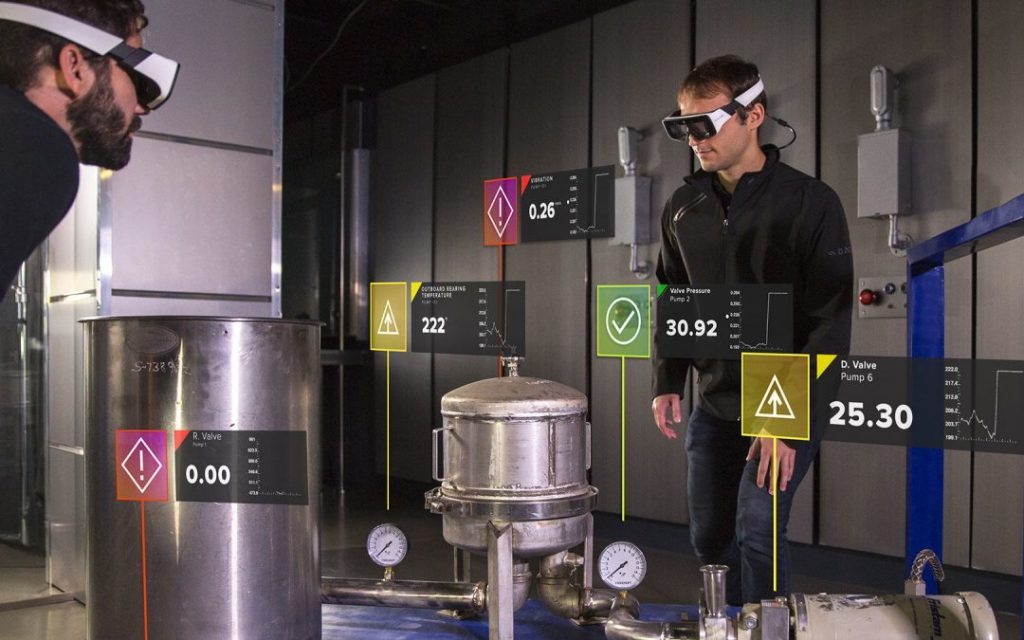
Augmented Reality allows users to enhance their field of view with real-time super imposed digital information. This allows users to gain any/all information on an asset or step by step instructions on how to repair an asset, for example.
But before we dig into practical applications, let’s discuss the proven advantages of augmented reality maintenance.
Benefits
- Reduced human errors
- Reduced execution time
- Reduced breakdowns
- Reduced downtime
- Reduced cost
- Increased productivity
- Increased operation speed
- Increased fix rates
- Increased compliance
- Increased profit
These benefits prove true for the companies below that have already implemented augmented reality technology in their facility.
GE Aviation – Experiences an average of 8-12% in efficiency
GE Renewable Energy – Wiring technicians are yielding a 34% increase in productivity
These are just two examples of how AR is impacting the industry, but much has changed since the origins of the industrial revolution. From physical documentation, moving to the desktop, to the progression of mobile, to now wearable devices/technology.
AR powered solutions for maintenance and repair operations include:
- Preventive Maintenance
- Operator assembly instructions
- Service inspection instructions
- Detailed instructions for unfamiliar procedures
- Compliance checklist
- Corrective Maintenance
- Service manual instructions
- Remote assistance
- Predictive Maintenance
- Performance Panels
- Real-time access to data: monitoring, control actions, disruptions, analytics
All the above have their own unique value, but let’s take a deeper look into the workforce and how AR is impacting engineers.
Technology in the Workforce
Facility managers are constantly looking at ways to increase productivity, decrease costs, and keep engineers safe on the job. These technologies below integrated with an EAM CMMS system can help achieve all those goals.
Infrared thermography allows engineers and mechanics to see electrical systems, mechanical equipment, building applications, and fluid systems through the use of thermovision. Engineers can spot faulty connections, abnormal motors, pipe temperatures and tank levels through this equipment showing different colors without having to touch the equipment. This reduces the risk of engineers getting hurt on the job.
A company called DAQRI is focused on AR technology and developed a wearable AR tech smart helmet for industrial use. Engineers can see 4D images above assets in their facilities that prompt them with instructions and also give them a mapping of all asset functionality. This wearable technology allows engineers to discover asset information faster and closes the knowledge gap for new hires.
Another company called UpSkill connects the workforce through augmented reality in its wearable technology guiding technicians in real-time to complete tasks, checklists, work orders, and send media to managers.
Finally, a company called Worklink has made it possible for the user to create their own smart instructions for assets to allow for less human error, increase safety, and also walk engineers step-by-step on repair processes. This can increase the time it takes to complete work by also complying with facility procedures.
This equipment is becoming more prevalent and as more machines becomes connected to the internet, approximately 50 billion machines will be connected on the internet by 2020 it becomes imperative facilities and industries adopt these devices and make them apart of their facility operations.
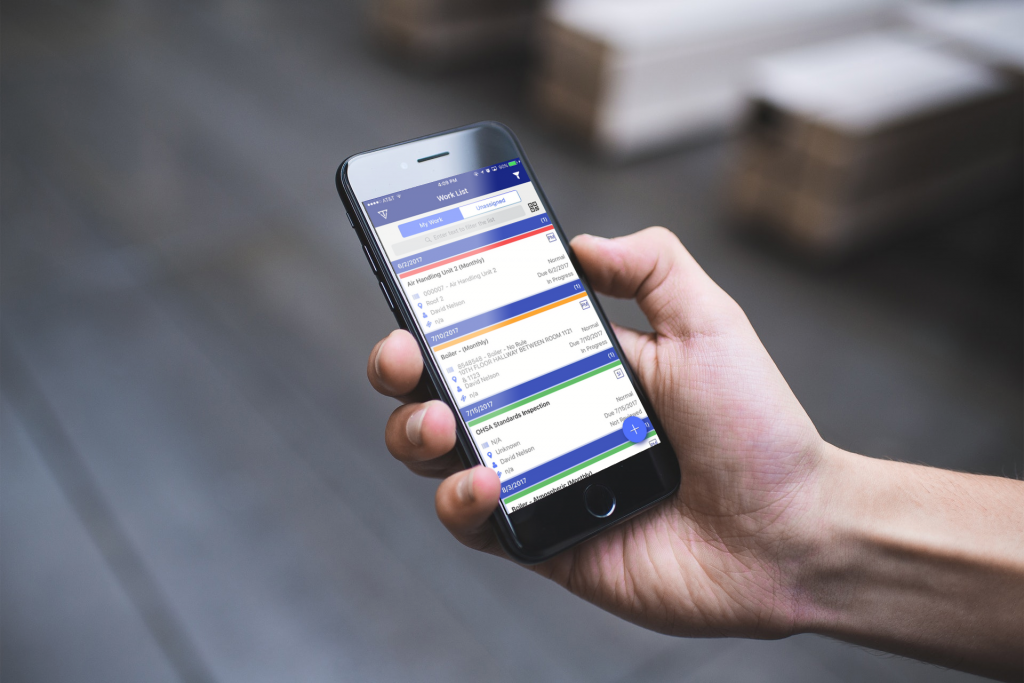
A CMMS has the capability to provide maintenance management and staff with an automated tool capable of scheduling inspections, preventive maintenance, managing inventory, work orders, and retrieval of recorded asset history.
Technicians can perform actual work with instructions on handhelds, enter how long it takes to complete work orders, filter through past work orders, and close out of the system. All the information is recorded in real-time, so managers can access the information instantaneously.
The ability to track your work, document it, and send it to managers could be paired with wearable technology, like the companies above, to get engineers an elevated view of assets through thermal technology or the ability to see instructions on assets and use that data to train new hires and not have to worry about on-boarding.
A CMMS could also benefit from machine learning using algorithms to monitor assets like meter readings and the ability to calculate readings by the second which would be humanly impossible to do; this will cut down on extraneous labor costs and allow facilities to allocate dollars elsewhere.
The possibilities are becoming endless when it comes to how IoT, AR, VR, and Machine learning can help facilities with energy savings, labor savings, employee safety, and more. The future is a scary and exciting thing but ultimately inevitable for change.